
Introduction: Operating drones in unstable terrains poses safety and logistical challenges. This Serious Game leverages Mixed Reality (MR) to simulate hazardous environments using Virtual Reality (VR) for training and Augmented Reality (AR) for collaborative analysis. Objective: This work develops an MR-based training simulation where players explore unstable environments, evaluate pre-planned drone trajectories, and predict terrain changes to improve flight strategy and risk assessment. Methodology: Players use VR to safely explore hazardous terrains, analyze drone data, and rehearse flight paths before real missions. The system gradually trains operators to transition to real drone use. A future AI prediction module is intended to enhance terrain analysis by anticipating environmental changes. AR supports strategic collaboration by enabling shared visualization and discussion of unstable environments. Expected Results: The game aims to enhance spatial awareness, improve flight planning, and support safer decision-making. It offers a risk-free environment to evaluate terrain evolution and drone strategies without field exposure.
Close Project
This paper addresses the challenge of finding the shortest path in complex environments by integrating machine learning and traditional algorithms to enhance path planning techniques. The goal is to strike a balance between path length and processing time, ensuring reliable trajectories for Unmanned Aerial Vehicles. We explore four methodologies: Reinforcement Learning, Sample-Based, Geometric-Based, and Polynomial-Based Methods. Our main focus is on harnessing Reinforcement Learning for its adaptability and experiential learning capabilities in complex environments, despite its known slow convergence and high computational costs. Our proposed algorithm optimizes each step of the standard Reinforcement Learning method, Q-Learning, using classical techniques to refine its core behavior and overcome limitations. Testing in various simulated complex and unknown environments demonstrates the algorithm’s efficacy in enhancing path planning efficiency and accuracy. Our approach successfully reduces path lengths by 11%, decreases flight time by 35%, and lowers processing time by 64% compared to the original Q-Learning approach.
Close Project
Precise tree measurement is essential for forest inventory and biomass estimation. Current methods often capture data only from the upper or lower parts of trees, resulting in incomplete or estimated measurement, bringing uncertainty to measurements. Some approaches fuse upper and lower tree data, but they require the alignment and merging of dense point clouds, making large-scale implementation challenging. This study presents an autonomous navigation and real-time data extraction method using an unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) equipped with depth cameras and a LiDAR sensor. The system navigates autonomously and maps the environment around it, using a uniform voxel grid to segment and measure individual trees. The results demonstrated that: (1) the UAV successfully navigates autonomously between trees, mapping the unstructured and unknown environment while performing real-time reconstruction; (2) tree trunk segmentation, measurement, and localization were achieved with an root mean square error (RMSE) of 0.22 m; and (3) tree height measurements obtained an RMSE of 0.05 m. The proposed methodology proved to be effective for forest inventory applications, providing accurate tree measurements with improved computational efficiency.
Close Project
Unmanned Aerial Vehicles need an online path planning capability to move in high-risk missions in unknown and complex environments to complete them safely. However, many algorithms reported in the literature may not return reliable trajectories to solve online problems in these scenarios. The Q-learning algorithm, a reinforcement learning technique, can generate trajectories in real-time and has demonstrated fast and reliable results. However, this technique has the disadvantage of defining the iteration number. If this value is poorly defined, it will take a long time or not return an optimal trajectory. Therefore, we propose a method to dynamically choose the number of iterations to obtain the best performance of Q-learning. The proposed method is compared to the Q-learning algorithm with a fixed number of iterations, A*, Rapid-Exploring Random Tree, Particle Swarm Optimization, Deep Q-learning, and Double Deep Q-Network. As a result, the proposed Q-learning algorithm demonstrates the efficacy and reliability of online path planning with a dynamic number of iterations to carry out online missions in unknown and complex environments.
Close Project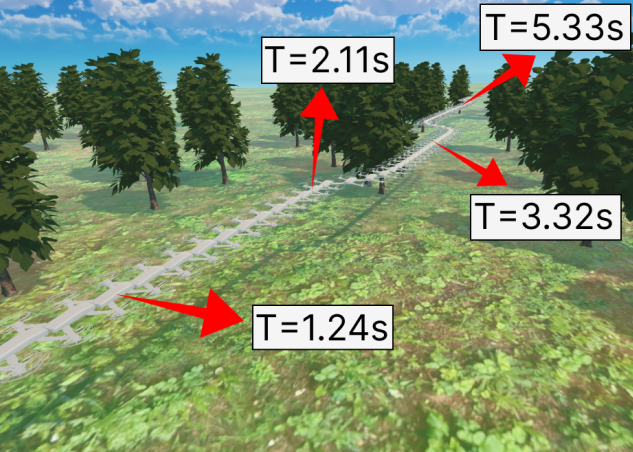
Unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs), known for their agile flight capabilities, require safe trajectory planning to achieve high-speed flights. This is necessary to swiftly evade obstacles and adapt trajectories under hard real-time constraints. These adjustments are essential to generate viable paths that prevent collisions while maintaining high speeds with minimal tracking errors. This paper addresses the challenge of enhancing the safety of agile trajectory planning. The proposed method combines a supervised learning approach, as teacher policy, with deep reinforcement learning (DRL), as student policy. Initially, we train the teacher policy using a path planning algorithm that prioritizes safety while minimizing jerk and flight time. Then, we use this policy to guide the learning of the student policy in various unknown environments. Testing in simulation demonstrates noteworthy advancements, including an 80\% reduction in tracking error, a 31% decrease in flight time, a 19% increase in high-speed duration, and a success rate improvement from 50% to 100%, as compared to baseline methods.
Close Project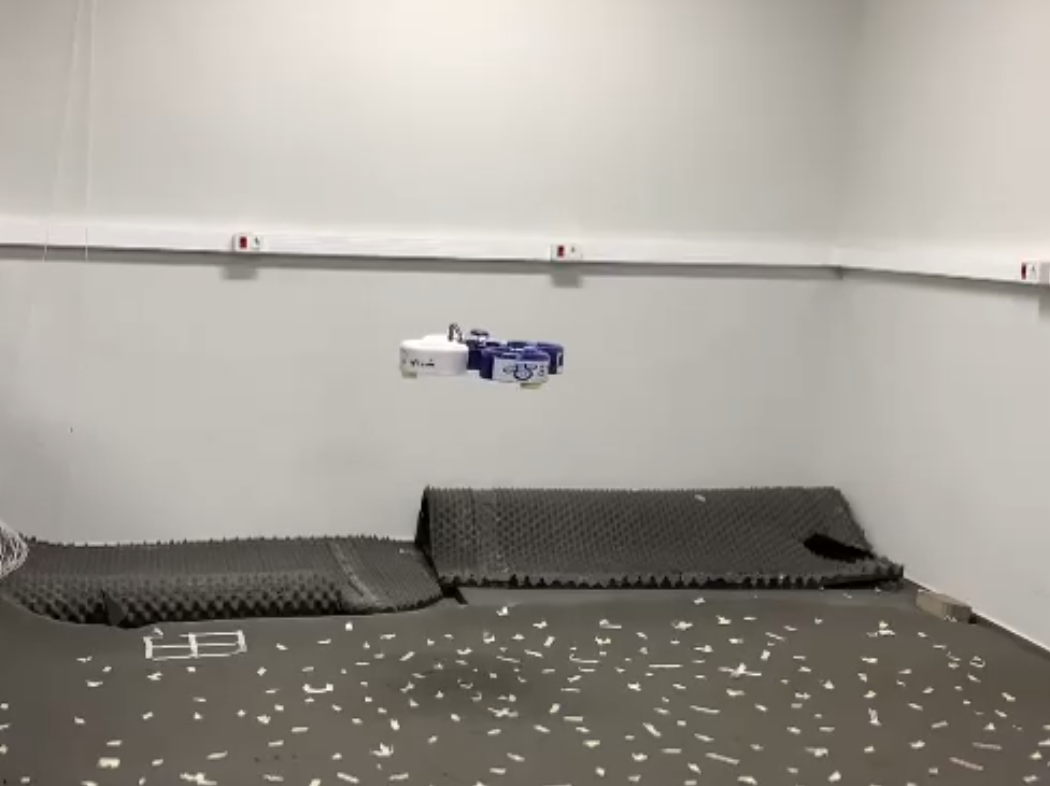
Aquatic macrophyte is a generic denomination for macro-algae with active photosynthetic parts that remain totally or partially submerged in fresh or salty water, in rivers and lakes. Currently, algae monitoring is carried out manually by collecting samples to send for laboratory analysis. In most cases, harmful algal blooms are already widespread when the results are disclosed. This paper proposes the application of a team of heterogeneous Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs) that cooperate to increase the system’s overall observation range and reduce the reaction time. Leader UAV, featured with a deep-learning-based vision system, covers a pre-determined region and determines high-interest inspection areas in real-time. Through a multi-robot Informative Path Planning (MIPP) approach, the leader UAV coordinates a team of customized quadcopter (named ART2) to reach points of interest, managing their route dynamically. ART2s are able to land on water, and collect and test samples in situ by applying phosphorescence sensors. While path planning, task assignment, and route management are centralized operations, each UAV is conducted by a decentralized trajectory tracking control. Simulations performed in a realistic environment implemented on the Unity platform and experimental proof of concepts demonstrated the reliability of the proposed approach. The presented multi-UAV framework with heterogeneous agents also enables the reconfiguration and expansion of specific objectives, in addition to minimizing the task completion time by executing different processes in parallel. This preventive monitoring enables a plague control action in advance, solving it faster, cheaper, and more effectively.
Close Project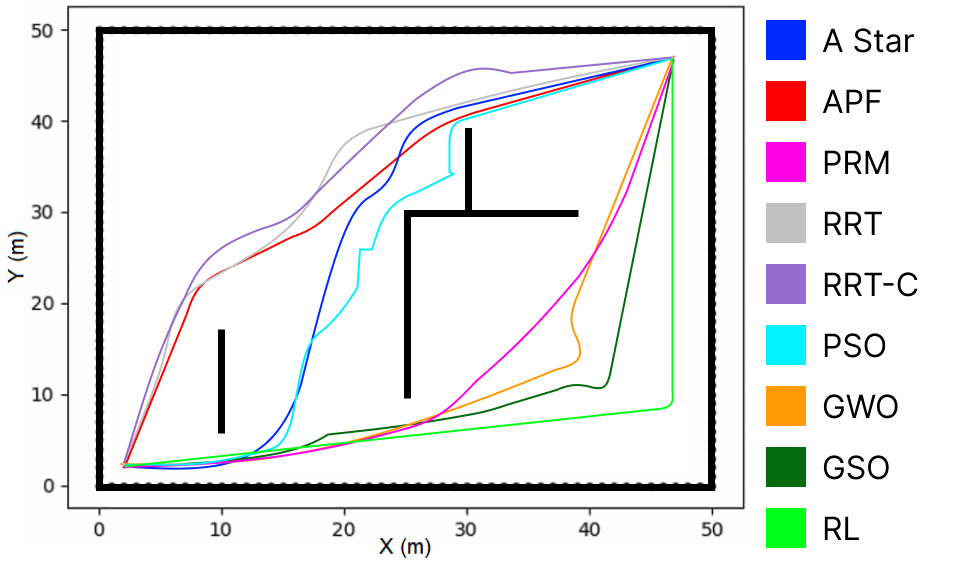
Autonomous robots can use path planning techniques to determine the optimal trajectory during the mission. These techniques can be classified as classical, meta heuristic, or machine learning-based. The choice of each technique for a mission depends on its specific requirements, such as finding the shortest path, completing the mission in the minimum time, or/and exploring the environment, among others. Therefore, the path planning algorithms analysis is essential to assist in selecting the appropriate technique. In the literature, the path planning algorithms are typically compared within the same category, and a general analysis is conducted to decide which technique to employ for a particular mission. However, this paper aims to delve deeper into the behavior and performance of these three path planning techniques. The analysis is based on simulations in various environments to understand how each technique behaves and performs, specifically focusing on computation costs, time, and path length efficiency.
Close Project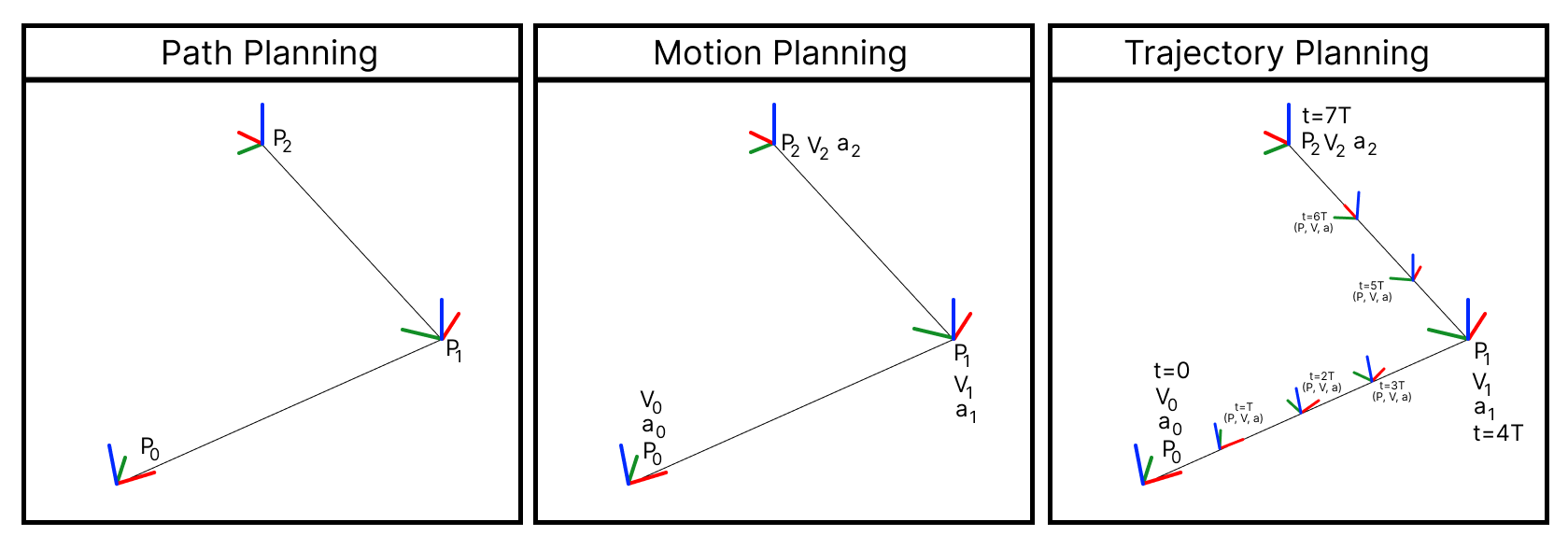
The use of autonomous unmanned aerial vehicles has increased for High-Speed flights, leading to the need for improved performance. Trajectory planning is the primary approach to achieving high speeds, as it is safer and more flexible than other planning types. Some approaches include polynomial trajectories, optimization-based, search-based, sampling-based, and artificial intelligence, mainly reinforcement learning. This paper provides an overview of the main techniques for high-speed trajectory planning in UAVs and the challenges associated with them. It also describes essential UAV dynamics, control, and perception to reach high speeds. These techniques are demonstrated in several missions and environments, describing their methodologies. Finally, we discuss the open problems and potential future research directions in this field.
Close Project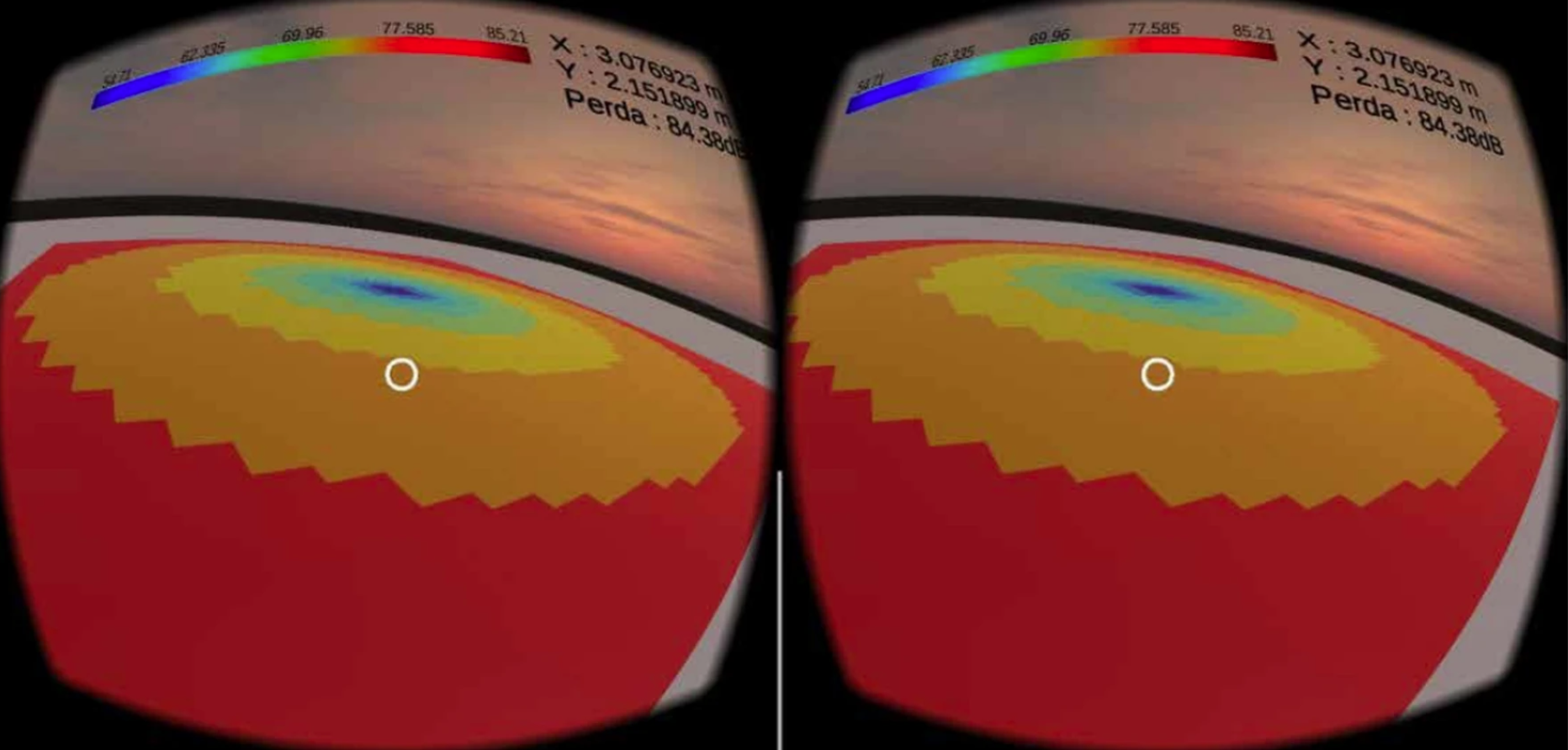
Society is increasingly connected, utilizing more data that demands greater capacity and better channel quality. Furthermore, wireless networks are being inserted into the population's daily lives. Therefore, solutions capable of transferring a high volume of data are increasingly needed. In this context, we present a framework that aims to network planning through data collection, modeling, and routers optimization in the environment. Ziwi framework can simulate wireless networks in indoor and outdoor environments with the main classical propagation models, obtain and calculate metrics and performance parameters. It is possible to measure data by cell phone and send it to the website quickly. Furthermore, it can model the data and compare with different propagation models. Also, optimize them using a genetic algorithm or permutation, choosing whether or not to consider sockets to turn on the routers and how many routers are needed to place in the environment. In addition, have a virtual reality environment aiming at greater interactivity with the data. We analyzed framework results comparing with Close-In propagation model, free space model, and statically using the root mean square error metric. Measurements were made in a real environment using the Ziwi mobile application, inserting data captured on Ziwi website to validate the framework.
Close Project
For an Unmanned Aerial Vehicle to become autonomous, it must perform actions without human interference. Regardless of its application area, path planning is required to carry out a mission. Nowadays, several applications require the UAV to operate in an unknown, 3D, and unstructured environment. Another essential point is considering the movement restrictions in the execution of the movements, where achieving smooth curves reduces the number of stops on 90 degrees curves. One observable aspect among the existing and most used techniques is” which would be the best technique to work in each of these environments”. This work aims to answer this question with a deeper analysis of all path planning categories: classic, metaheuristic, and machine learning. We develop our planner to analyze these techniques considering completeness, distance, time, CPU usage, memory usage, collision prevention, and robustness. This planner is modular, so it is possible to add new techniques and scenarios to be studied. We also performed tests in simulated and real environments.
Close Project
Over the years, research has enabled robots to become more autonomous, determining their trajectories. Thus, path planning is an important area in autonomous robots. With the growing number of path planning algorithms, it is essential to have a framework capable of analyzing several algorithms in the same scenario to assess their capabilities. This paper presents Plannie, a framework to develop, simulate, benchmark, and test path planning algorithms in 2D and 3D environments in the real world. It supports many path planning algorithms, such as classic, metaheuristic, and machine learning. Furthermore, this framework offers several maps from an external database. However, it is also possible the build new maps in addition to having control, mapping, and localization techniques available for testing in a real environment. Plannie also offers planning modules that involve dynamic obstacle avoidance, coverage, traveling salesman problems, and multi-robot algorithms. Finally, we demonstrate the capability of the Plannie benchmarking several path planning algorithms in different maps. Plannie is open-source.
Close Project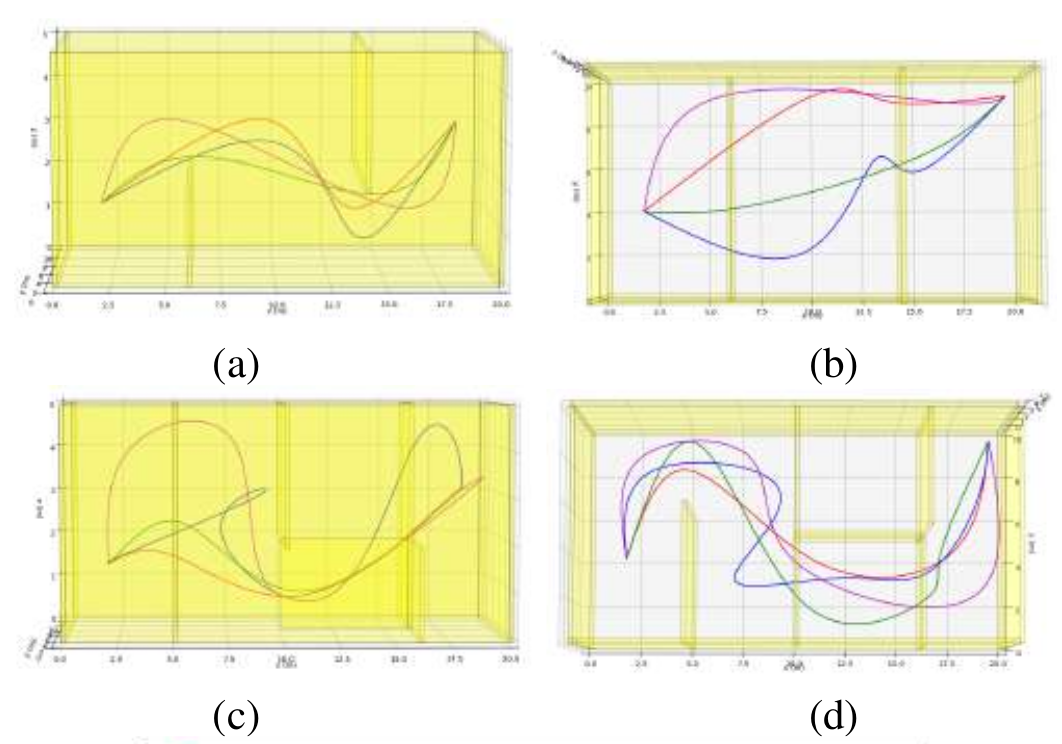
Unnamed Aerial Vehicles can carry out several missions. It is essential to use path planning algorithms to obtain an efficient trajectory without collision to complete these missions. Several path planning algorithms in the literature are divided into four categories: exact classic, approximate classic, meta heuristic, and machine learning. However, it is not easy to define which is the best for each mission among all path planning algorithms. In this context, an analysis between these categories can facilitate research determining the techniques that obtain better results in each UAV mission. So, in this work, we perform a deep benchmarking of 3D path planning techniques in a simulated and real environment. As a result, classical techniques demonstrate better capacities in dynamic path planning. On the other hand, meta heuristic and machine learning techniques performed the best results for static path planning.
Close Project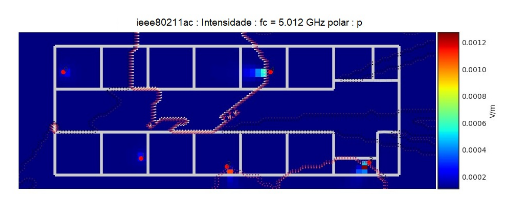
This article uses the open source simulator PyLayers, developed in Python language, which allows its customization, so in this work a simulation was done in an indoor environment with access points (APs) using the IEEE 802.11ac standard and through electric field graphs it was possible to verify the level of electromagnetic exposure to which users were submitted and was subsequently evaluated if the levels were within the safety limits defined by National Telecommunications Agency.
Close Project
Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV) has been increasingly employed in several missions with a pre-defined path. Over the years, the use of Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAV) has become necessary in complex environments, where it demands high computational cost and execution time for traditional algorithms. To solve this problem meta heuristic algorithms are used. Meta heuristics are generic algorithms to solve problems without having to describe each step until the result and search for the best possible answer in an acceptable computational time. The simulations are made in Python, with it, a statistical analyses was realized based on execution time and path length between algorithms Particle Swarm Optimization (PSO), Grey Wolf Optimization (GWO) and Glowworm Swarm Optimization (GSO). Despite the GWO returns the paths in a shorter time, the PSO showed better performance with similar execution time and shorter path length. However, the reliability of the algorithms will depend on the size of the environment. PSO is less reliable in large environments, while the GWO maintains the same reliability.
Close Project
A good performance for path planning is essential to carry out real-world missions. In this paper, the path planning consists of a global planner, that finds the optimal path, and in a local planner, recalculates the path to avoid obstacles. The main focus is to improve the performance of local planning techniques decreasing the complexity. There are two main ways to do it: bidirectional algorithms, improving time, and global planners, improving time and completeness. Thus, we propose a global planner algorithm that generates auxiliary nodes, backtracking by the goal node. We perform a comparison among A*, Bi A*, Artificial Potential Field (APF), Bi APF, Rapid Exploring Random Tree (RRT), and Bi RRT with and without the global planner through statistical metrics of time, path length, CPU, and memory. The results show the advantages of using bidirectional algorithms and the proposed global planner. The bidirectional algorithms decrease the time to return to the trajectory and sometimes assist in the algorithm's completeness. The proposed global planner reduced the planning time by 91.6% and improved the completeness of all algorithms in an unstructured indoor environment.
Close Project
When young people enter engineering courses, they are usually excited and motivated to do new projects and learn how to use different technologies. However, most of them come from regular schools, without having taken any technical course in the area, and consequently without the necessary knowledge to develop the idea you want. Although there is a lot of content available on the internet, most of it is disorganized, unintuitive and in a foreign language. With this situation in mind, a website was built where these young people can exchange ideas about their projects together with other people who are also facing the same reality, doing similar projects without effective support.
Close Project
This game aims to help children's learning from gamification, having characteristics to earn extra points for the students' grades, encouraging them to improve in school to gain new talents and unlock items in the game and thus compete on equal terms with their friends. It was defined as a mobile game because it takes into account the growth in the sector today and because of its portability compared to other means, in addition to being the most practical way to encourage the use of the game by students at school as supplementary and encouraging material for studies of them. With this system, the aim is to improve the engagement of young people in basic subjects, so when they enter high school they do not feel the basic requirements of the subjects are missing, reducing their difficulty during the school period through games.
Close Project
This paper presents an alternative way to play video game interactively. To construct the control of the game, it will be used cardboard to build the structure, aluminum foil for the contact with the microcontroller, and a microcontroller, that will be an Arduino based on ATMega 32U4. To attract the attention of the public, will be developed games different than conventional, being the first a race in outer space. To test the viability of the project, a pilot test was made with the Makey Makey board that would build an Atari control made with cardboard to replace the computer mouse.
Close Project
This paper presents the use of an artificial neural network in pattern recognition. To validate its applicability, the determination of the starter pok ́emon based on the personality of the player was used as a theoretical problem. To solve the problem, a multi-layered neural network using a RPROP learning algorithm was developed.
Close Project
This article presents the steps to develop a 3D module, an extension added to the Simulator for Mobile Communication Network Planning. Through the code developed for the tool and the guidelines of Resolution No. 303 of the National Telecommunications Agency, of July 2002, the original code was restructured, the module created in accordance with the norms and the creation of new antennas for the virtual environment . Using Virtual Reality techniques present in the tool, it is possible to build scenarios, configure antennas and collect data that make it possible to assess whether a certain area is receiving radiation or not. In the module, it is possible to see the value of the transmission power, the field strength, the antenna being analyzed, the transmission frequency, whether the environment is receiving radiation or not, as well as the threshold allowed by ANATEL.
Close Project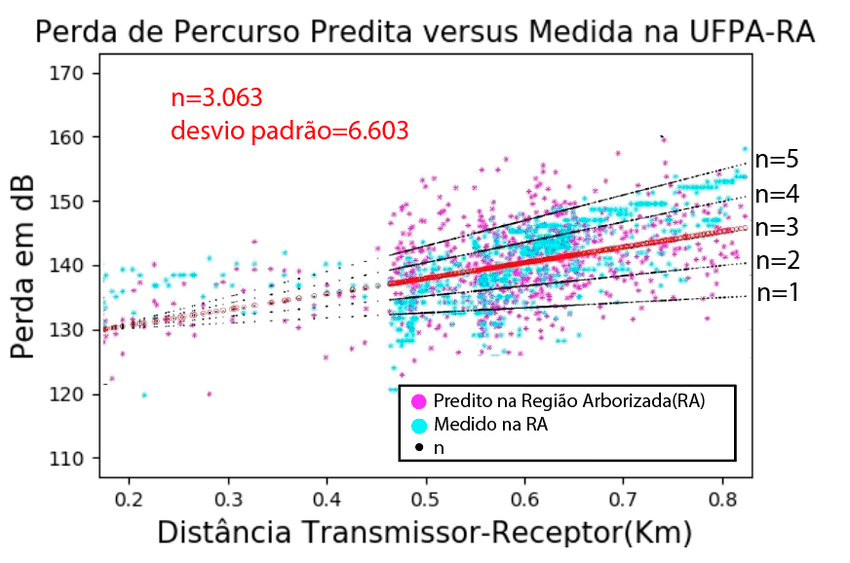
In this work, the Standard Propagation Model (SPM) path loss prediction model was adjusted using a genetic algorithm (AG) and the propagation characteristics of a wooded area in the city of Belém-Pará in the frequency range of 2 were also analyzed. .6 GHz. The article also makes a comparative analysis with classical models such as Free Space Model, Okumura-Hata Model, Walfisch-Ikegami Model, COST 231 Model, Ericsson Model 9999, ECC-33 Model, SUI Model and Extended SUI Model using the Matlab software. It will be described how SPM can be calibrated and applied as a radio planning tool in a given forested area. For that, a measurement campaign (drive test – DT) was carried out in the city of Belém-PA in a wooded area. SPM and WalfischIkegami showed the smallest path loss error for the wooded area compared to all other propagation models.
Close Project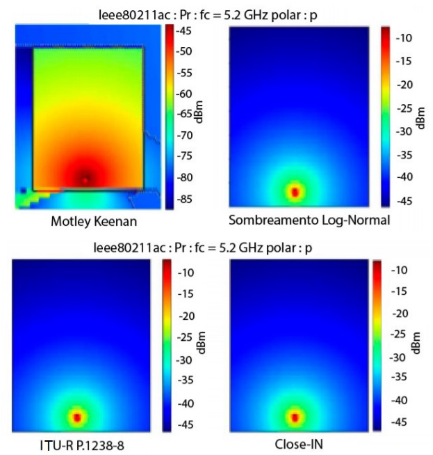
Wi-Fi networks have evolved from IEEE 802.11a to current networks, namely, IEEE 802.11ac, and may reach higher speeds than wired networks as proposed by the new IEEE 802.11ay standard [1]. Therefore, in order to assess the implementation proposed by this article, the IEEE 802.11ac standard was chosen in a laboratory environment to evaluate the coverage characterization and customization tests performed in PyLayers. This customization made it possible to carry out radiopropagation simulations on IEEE 802.11ac networks in various indoor environments and plot heat maps of coverage and path loss. For this, propagation models were added to it, in order to represent the simulation scenario.
Close Project
This article presents a large-scale modeling analysis for different types of corridors at 10 GHz, within line-of-sight (LoS) conditions, including behavioral statistics for the received signals. Influenced by structural and material conditions, there is a 2dB increase for the stone-walled corridor, demonstrating that multipaths generated by the environment's material permittivity are directly related to signal loss. This work contributes to the evaluation of mmWave communication performance when applied to fifth generation (5G) systems.
Close Project
In the near future the millimeter waves will begin to be commercialized, and the understanding of how they work needs to be known by the scientific and commercial community. For this reason, a simulator representing these new networks is necessary. Currently, a simulator that can predict the best locations for wireless routers has not been found. Therefore, a simulator is being developed capable of measuring and predicting signal level data from an indoor environment to next generation networks considering existing propagation models and some already proposed for this frequency range.
Close Project
Wireless communication is the most common method for accessing internet, and can be done through cell phones, notebooks, or other devices that need to be connected to an access point. Although, a wireless network (WLAN) needs to be well planned to provide good coverage, data transmission and reception capacity. To improve the coverage in a specific area, many factors need to be optimized simultaneously. This article presents an evaluation metric for obtained through simulations for analysis of coverage and capacity of a WLAN network in the rectory of the Federal Rural University of Amazonia (UFRA). Coverage calculation is based on the propagation model indoor of Motley Keenan, considering that the Access Points (APs) used are in the IEEE 802.11ac with 5.8 GHz.
Close Project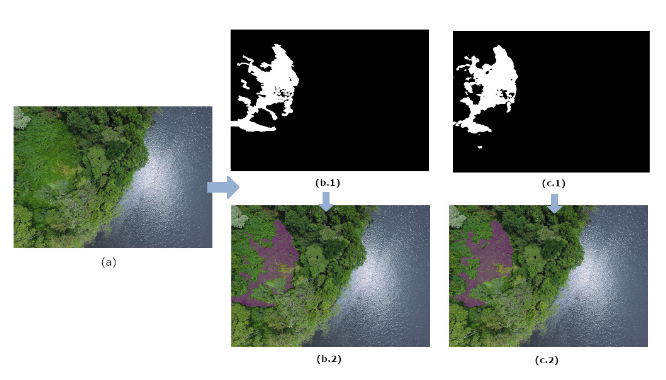
Species originating from one biome are often irregularly introduced into other biomes by accident. This event configures a biological invasion, which can cause irreversible adverse impacts on biodiversity and affect economic productivity in sectors such as fisheries, forestry, and agriculture. Furthermore, many species are vectors of human diseases, making biological invasions a significant problem. In Brazil, monitoring becomes very complex, with many closed forests, such as the mountain regions and other places with difficult accessibility, and demands many resources to maintain it, whether human or financial. Remotely and autonomously detecting invasive vegetation in large or complicated physical access areas can positively impact conservation work. Governments can take concrete actions to favor the environment through this monitoring and avoid irreversible damage to the ecosystem. Therefore, this paper proposes the classification of images using Deep Learning algorithms to detect the invasive species Hedychium Coronarium. We will capture the photos by remote sensing through UAVs (Unmanned Aerial Vehicles).
Close Project
Several environmental problems requires constant monitoring to ensure that the human interference is not changing the natural habitats. This kind of effort requires many hours of human labor to be performed manually and has a cost associated with it. This work proposes a framework for managing the UAV tasks of creating routes for scanning and sampling algae overgrowth issues in water bodies and makes a comparison between an offline and an online planning strategy that will be tested in a simulated environment.
Close Project
Human-Robot Interaction (HRI) will be a crucial component of intelligent factories of the future (FoF). Nevertheless, several research indicates that robot teleoperation can be challenging and, therefore, impose high requirements on user training and expertise. The emerging technology of Extended Reality, the umbrella for immersive technologies associated with different types of realities, has recently been applied to create novel developer tools in industrial robotics, with the potential to increase user-friendliness and minimize requirements on user training and operator’s previous expertise. This paper evaluates the robot teleoperation efficiency achieved by a number of users performing a given task, using the traditional keyboard method and two forms of extended realities. Results showed the advantages of teleoperation based on extended realities, with respect to user friendliness, less operational errors, and efficiency and effectiveness.
Close Project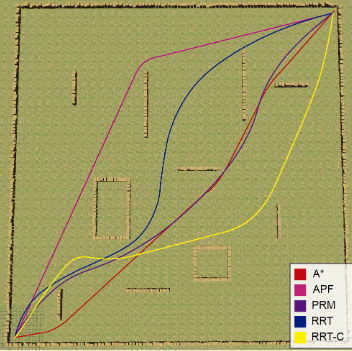
Unmanned aerial vehicles have been increasingly used to solve problems in several areas. These problems require the UAV to move between two nodes precisely to perform the tasks. In this way, path planning algorithms are adopted to provide this path. The classic algorithms can confirm whether a result exists or not and be great for flying in real-time. However, there are many classical algorithms, and each of them has better performance in different environments. Therefore, this paper presents a comparison and statistical analysis between the classical algorithms, emphasizing the best algorithms, showing the advantages and disadvantages of each algorithm in indoor and outdoor environments. The algorithms that presented better performance are tested in a 3D environment. The analyzed algorithms are A*, Artificial Potential Field, Probabilistic Random Map, Rapid Random Tree, and Rapid Random Tree Connect. We validate the results in 2D and 3D simulations, in Python, and on Gazebo.
Close Project
The lack of monitoring of traffic by public policies is one of the main problems that affect Pará with regard to urban mobility. The population that is unable to invest in private transport is a victim of this bad condition. Submitted to a public transport system that leaves a lot to be desired, they often suffer for long periods of time until they are able to board the bus they want. Seeking to alleviate this problem, the research and development team of the Laboratory for the Development of Ideas (LDI) at the Federal University of Pará (UFPA) proposes a system that estimates the waiting time until the vehicle arrives, the transfer time to the destination , as well as seeking to collect statistical data to improve urban traffic management. Information of interest to the citizen can be accessed by the same through mobile and web applications developed by the team. This article seeks to explain how the proposed system works.
Close Project